Download From Internet Mac Terminal To Another Server
Applies to RouterOS:2.9, v3, v4
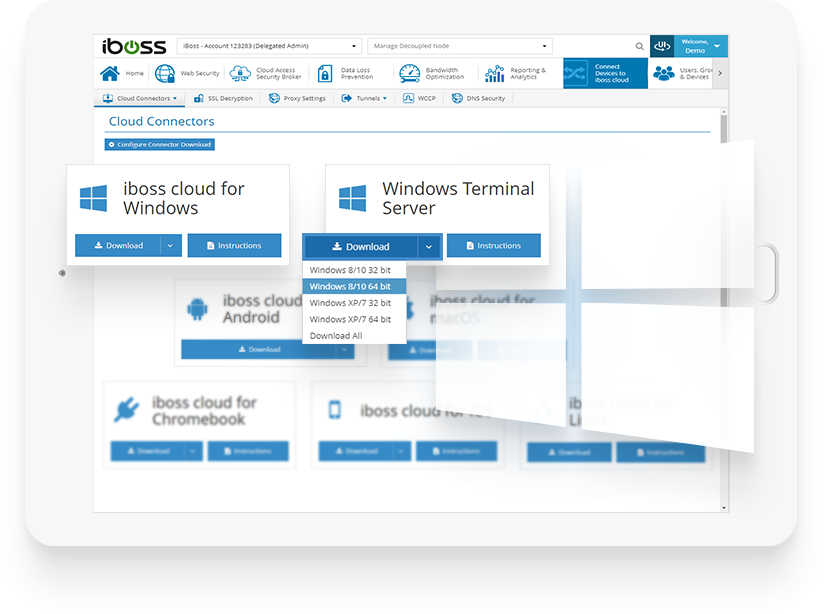
Terminal server in Windows 1 –Download and install the Microsoft Remote Desktop app. This is free and available for download via the the OS X App Store. 2 - Connect to the System VPN client using the Pulse Secure VPN client installed on your workstation. This step is required in order to connect to a remote computer or terminal server. Apr 12, 2012 Apple Footer. This site contains user submitted content, comments and opinions and is for informational purposes only. Apple may provide or recommend responses as a possible solution based on the information provided; every potential issue may involve several factors not detailed in the conversations captured in an electronic forum and Apple can therefore provide no guarantee as to the. I installed Ubuntu Server instead of Ubuntu Desktop because I wanted to run a lightweight Linux environment, which should save laptop resources. I simply run the VM in the background, and ssh into it from the Mac terminal. Easy and awesome! This entire tutorial should take approximately 20 minutes (not including download times). Install VirtualBox.

MAC telnet is used to provide access to a router that has no IP address set. It works just like IP telnet. MAC telnet is possible between two MikroTik RouterOS routers only.
- 2MAC Telnet Server
- 3MAC WinBox Server
- 4MAC Scan
- 5MAC Telnet Client
Specifications
- Packages required: system
- License required: Level1
- Submenu level: /tool, /tool mac-server
- Standards and Technologies: MAC Telnet
- Hardware usage: Not significant
MAC Telnet Server
- Submenu level: /tool mac-server
Property Description
- interface (name | all; default: all) - interface name to which the mac-server clients will connect
Notes
There is an interface list in this submenu level. If you add some interfaces to this list, you allow MAC telnet to that interface. Disabled (disabled=yes) item means that interface is not allowed to accept MAC telnet sessions on that interface. all interfaces iss the default setting to allow MAC teltet on any interface.Example
To enable MAC telnet server on ether1 interface only:
MAC WinBox Server
- Submenu level: /tool mac-server mac-winbox
Property Description
- interface (name | all; default: all) - interface name to which it is alowed to connect with Winbox using MAC-based protocol
Notes
There is an interface list in this submenu level. If you add some interfaces to this list, you allow MAC Winbox to that interface. Disabled (disabled=yes) item means that interface is not allowed to accept MAC Winbox sessions on that interface.Example
To enable MAC Winbox server on ether1 interface only:
Download From Internet Mac Terminal To Another Server Hosting
Monitoring Active Session List
- Submenu level: /tool mac-server sessions
Property Description
- interface (read-only: name) - interface to which the client is connected to
- src-address (read-only: MAC address) - client's MAC address
- uptime (read-only: time) - how long the client is connected to the server
Example
To see active MAC Telnet sessions:
MAC Scan
- Command name: /tool mac-scan
This command discovers all devices, which support MAC telnet protocol on the given network.
Property Description
- (name) - interface name to perform the scan on
MAC Telnet Client
Command name: /tool mac-telnetProperty Description(MAC address) - MAC address of a compatible device
Example
Terminal User Guide
In Terminal, you can move and copy files locally or remotely using the mv, cp, and scp command-line tools.
Tip: It’s easier to move and copy files using the Finder. See Organize files in folders.
Move a file or folder locally
In the Terminal app on your Mac, use the
mvcommand to move files or folders from one location to another on the same computer. Themvcommand moves the file or folder from its old location and puts it in the new location.For example, to move a file from your Downloads folder to a Work folder in your Documents folder:
% mv ~/Downloads/MyFile.txt ~/Documents/Work/MyFile.txtYou can also change the name of the file as it’s moved:
% mv ~/Downloads/MyFile.txt ~/Documents/Work/NewFileName.txt
See the mv command man page.
Copy a file or folder locally
In the Terminal app on your Mac, use the
cpcommand to make a copy of a file.For example, to copy a folder named Expenses in your Documents folder to another volume named Data:
% cp -R ~/Documents/Expenses /Volumes/Data/ExpensesThe
-Rflag causescpto copy the folder and its contents. Note that the folder name does not end with a slash, which would change howcpcopies the folder.
Mac Terminal Alternative
See the cp command man page.
Copy a file or folder remotely
Download From Internet Mac Terminal To Another Server Hosting
In the Terminal app on your Mac, use the
scpcommand to copy a file or folder to or from a remote computer.scpuses the same underlying protocols asssh.For example, to copy a compressed file from your home folder to another user’s home folder on a remote server:
% scp -E ~/ImportantPapers.tgz username@remoteserver.com:/Users/username/Desktop/ImportantPapers.tgzYou’re prompted for the user’s password.
The
-Eflag preserves extended attributes, resource forks, and ACL information.The
-rflag, which isn’t used in this example, causesscpto copy a folder and its contents.
Where Is Mac Terminal
See the scp command man page.